Induction Heating was first noted when it was found that heat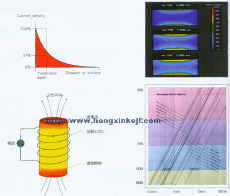
was produced in transformer and motor windings, as mentioned in the
Chapter “Heat Treating of Metal” in this book. Accordingly, the theory of
induction heating was studied so that motors and transformers could be
built for maximum efficiency by minimizing heating losses. The development
of high-frequency induction power supplies provided a means of
using induction heating for surface hardening. The early use of induction
involved trial and error with built-up personal knowledge of specific
applications, but a lack of understanding of the basic principles. Throughout
the years the understanding of the basic principles has been expanded,
extending currently into computer modeling of heating applications and
processes. Knowledge of these basic theories of induction heating helps to
understand the application of induction heating as applied to induction
heat treating. Induction heating occurs due to electromagnetic force fields
producing an electrical current in a part. The parts heat due to the resistance
to the flow of this electric current.

was produced in transformer and motor windings, as mentioned in the
Chapter “Heat Treating of Metal” in this book. Accordingly, the theory of
induction heating was studied so that motors and transformers could be
built for maximum efficiency by minimizing heating losses. The development
of high-frequency induction power supplies provided a means of
using induction heating for surface hardening. The early use of induction
involved trial and error with built-up personal knowledge of specific
applications, but a lack of understanding of the basic principles. Throughout
the years the understanding of the basic principles has been expanded,
extending currently into computer modeling of heating applications and
processes. Knowledge of these basic theories of induction heating helps to
understand the application of induction heating as applied to induction
heat treating. Induction heating occurs due to electromagnetic force fields
producing an electrical current in a part. The parts heat due to the resistance
to the flow of this electric current.
