How Induction Brazing Works
Views Send Enquiry
Induction brazing is a process where two or more materials such as pipe are joined together with a molten space filler metal using an induction heating coil which delivers a very high temperature. The induction brazing process will involve temperature more than 840 cengrade degree but still it is have to below the temperature of the material (such as pipe). By the induction brazing process the join materials will have very strong permanent attachment.The technology of brazing process itself has developing nowadays. New products and techniques of this metallurgical joining are discovering to enhance the performance, quality and cost effective that includes induction brazing method. In the last decades, brazing products and methods have been developed, including oxygen-acetylene torches, controlled environment brazing furnaces and vacuum furnace brazing and induction brazing. Today, brazing is used in a broad range of manufacturing systems including refrigeration and air-conditioning, household utensils, tubular structures, automotive parts, tools and machinery, electrical components, nautical and aerospace equipment, farm implants, and business machines.To get the best quality and best cost effective brazing result is to have a best heating technique to ensure the best flow of filler metal in between the join of the material. In today demands the brazing process will also involve in a production line which a unique of brazing method is necessary to achieve best quality and cost effective. Therefore a unique induction brazing is widely using in such workIn induction brazing method temperature are usually reached in a matter of seconds for higher manufacturing productivity. The induction brazing method uses magnetism to induce electrical resistance to heat up the base material. Induction heating in induction brazing has proven an important tool in these joining processes. It allows for rapid localized heating, joining high-strength components with minimum loss of strength. An exact heat control in induction brazing allows the brazing process to be performed efficiently.Induction brazing alloys melt at high temperatures and provide high strength joints that can resist reasonably elevated temperatures without failure. Many of the alloys used for brazing are presented in the form of wire, strip, powder and also washers or rings for induction brazing process purposes.The design of the induction coil must be made to order to behavior of the metals and the dimension and shape of the joining parts. When using the induction brazing, special concern must also be given to the heating pattern; the method of pre-placing the joining alloy; the tolerances between mating parts; the thermal conductivity; and the expansion characteristics of the material to be joined.It is important that when designing brazing process (such in induction brazing) to consider the join strength which to have the maximum strength. This can be accomplished, in many instances, by pre-placing the joining alloy in such a way that it will flow into the joint by gravity and capillary attraction, showing uniform and complete penetration by appearance of the alloy at the opposite end of the joint.
Choice of the right form of brazing alloy is one of the most important issues which affects the integrity of any joint assembly- other factors being joint design and proper fit; cleaning procedure to prepare surface; fluxing practice; proper cooling and flux removal; and method of heating. So, how to choose just the right form of brazing alloy? Let’s know about it.Some Criteria to Choose Brazing Alloy!A brazing alloy is the metal which is added during the brazing process in order to complete a joint. Melting range for a brazing alloy has been defined by the minimum temperature at which the alloy starts melting (“solidus”) and the temperature at which the alloy becomes liquid (“liquidus”). For most purposes, the actual brazing temperature lies within 50癋 to 200癋 (30癈 to 110癈) above the liquidus. While the melting range depends upon the chemical composition of alloy, it is also important to note that individual batch characteristics may differ slightly. Some alloys have a very narrow melting range and others have a relatively wider range. Those having narrow melting range are used for filling very narrow gaps while others with wider range are better used for filling larger gaps.There are many forms of brazing alloys. Different alloy combinations change the melting temperatures as well as other properties of brazing alloy. However, a brazing alloy should fulfill the following basic criteria.It should flow evenly across the surfaces of the base metal, and through capillaries even if they are as small as 0.001-inch;It should resist alloy separation into solid and liquid phase during brazing.It should provide a strong bond by partially alloying with the base metals.It should meet conditions of corrosion resistance, ductility, thermal and electrical conductivity, or other desired properties.High temperature brazing alloys like gold, nickel and copper can be used for brazing multiple joints at a time but care must be taken with the joint design and joint clearance. In such cases, heating time should be minimized to the time needed to bring all components to the heating temperature and for the molten alloy to flow quickly. high temperature brazing should be used for joining cobalt or nickel-based superalloys.Although copper, nickel and silver are the most frequently-used base metals for brazing alloys; aluminum and gold are also used for some brazing applications. Most of the brazing alloys are generally available in various forms like wire, foil, tape, powder and paste. Know about all such forms of brazing alloys.

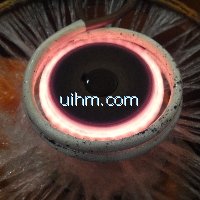
induction brazing
Hot

Relationship between induction frequency and quenching depth (hardening depth)
waveform of DSP induction heaters
simulation of Faradays Law from University of Colorado Boulder
optimizing induction welding method for vehicle air conditioner
induction welding vehicle air conditioner vs common welding method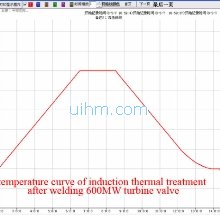
temperature curve of induction thermal treatment after welding 600MW turbine valve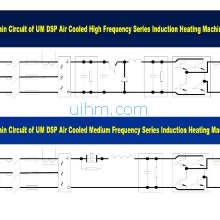
Main Circuit of UM DSP air cooled induction heaters
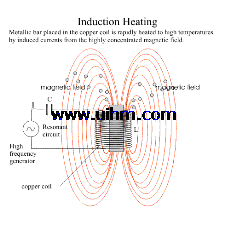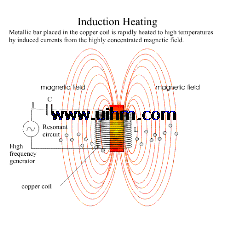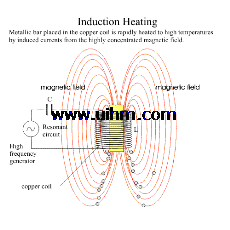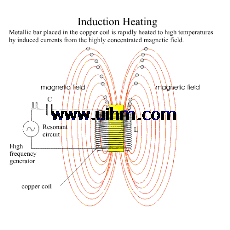
what is skin effect principle (magnetic force around induction coil)







Newest Comment
No Comment
Post Comment